Biodiversity
Biodiversity is not only the sum of all ecosystems, species and genetic material; it also represents the variability within and among them.
Definition of Biodiversity
The Convention on Biological Diversity gives a formal definition of biodiversity: "Biological diversity means the variability among living organisms from all sources including, inter alia, terrestrial, marine and other aquatic ecosystems and the ecological complexes of which they are part; this includes diversity within species, between species and of ecosystems".
Biological diversity is often understood at three levels:
- species diversity refers to the variety of different species (plants, animals, fungi and microorganisms) such as palm trees, elephants or bacteria;
- genetic diversity corresponds to the variety of genes contained in plants, animals, fungi and micro-organisms. It occurs within a species as well as between species.
- ecosystem diversity refers to all the different habitats - or places - that exist, like tropical or temperate forests, hot and cold deserts, wetlands, rivers, mountains, coral reefs, etc. Each ecosystem corresponds to a series of complex relationships between biotic (living) components such as plants and animals and abiotic (non-living) components which include sunlight, air, water, minerals and nutrients.

Marine Environment
British Gibraltar Territorial Waters are closely monitored in order to ensure the preservation and improvement of our waters as well as the life within. From marine management and coastal water monitoring to fishing regulations, this is addressed.
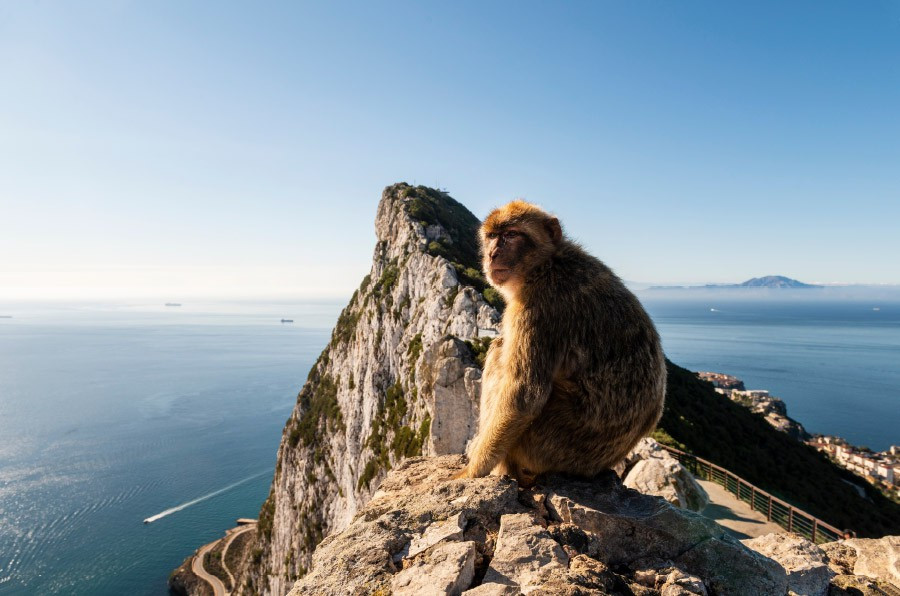
Rock of Gibraltar Nature Reserve
The Gibraltar Nature Reserve has evolved and developed significantly since the Upper Rock was officially designated as a Reserve in 1993. As part of the continued effort to further protect biodiversity and natural habitats in Gibraltar, the then Upper Rock Nature Reserve was rebranded and its size extended in 2013 to include new areas that would further help protect important habitats and species.


Urban Planning
Protecting and restoring wildlife habitat in cities is a vital component of wildlife conservation and there are lots of reasons to support urban biodiversity. On a purely practical level, these plants and animals provide valuable ecosystem services such as control of pests and the processing of air and water pollution.

